In this article, I will show you how can attacker bypass the advanced IDS/IPS sensor using invalid TCP checksum method.
Hope everyone is aware how the packet will be transferred over the network, if not let me brief in small line, when you send message over network, it doesn’t send in one huge packet whereas its broken into different stream of packets and transmitted. The application at the receiving end which receives the packets would be able to put the all the packets together.
The above concept applies to remote execution commands as well, remote commands sent by the attackers are not sent in single block and they are broken down into different streams and once receiving end reassembles it computer is able to execute them by then to detect/block remote execution commands IDS/IPS are placed in between the network to protect the server.
Tools like IDS are usually configured for speed and efficiency, TCP checksum used to ensure the data in TCP header and TCP payload have not be corrupted during transition, receiving and sending host performs TCP header checksum to validate the packets, hence IDS/IPS Sensors usually don’t calculate the checksum for performance reasons.
As checksum process will slowdown the tools, attacker take advantage of this loophole and send RST with a bad checksum so when your IDS/IPS sensor monitoring the traffic and respond it “Oh it is reset then I can clear my buffer memory and let me look for new packets, which means that slowing down to calculate checksums is often something these tools do not do. So, the attacker sends a RST with a bad checksum. Let me brief you with an example as show in below image.
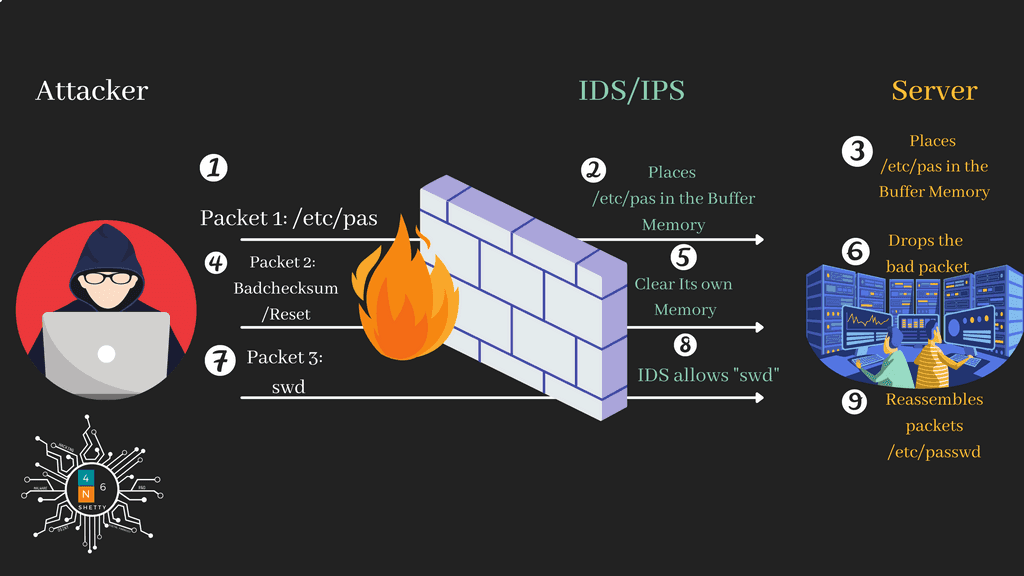
- The attacker sends first stream of packets "/etc/pas" to the protected server.
- When the IDS looks for at the /etc/pas and place in its buffer memory
- The server receives all packets and keeps first one “etc/pas”.
- The attacker sends badchecksum/reset packets to the server,
- The IDS, watching the traffic sees it and says "oh, a reset, I can clear my buffer and look at something new." This means, it is going to "forget" that it just saw the "etc/pas" packet that past through before the reset.
Note: The badchecksum/reset is packet is received and as said IDS is not usually configured to calculate the checksums, so its sees only portion of the packet. The IDS "assumes" that the connection is about to close and clears ITS OWN memory, preparing for a new set of packets.
- The badchecksum/RST packet that was allowed through the IDS will arrive at the server and server actually going to calculate the checksum and since its bad packet it will drop it. The connection that the IDS assumed was going to close remains open because the server dropped the reset packet which means that the server remembers the "etc/pas” .
- The attacker sends last stream of packets "swd"
- when it receives new set of packet (swd) it doesn’t see any threat because swd itself not a full command, the IDS will find nothing threatening about it and will let it pass through.
- So let me clear it, the server receives all three packets and keeps first one “etc/pas" and second packet badchecksum is dropped at the end "etc/pas" wil be waiting for other packets "swd" to come in, to reassemble into full command "etc/passwd"
This attack is completely dependent on the IDS being configured to handle the checksums. If the IDS calculate checksums, it does not reset its buffer and it sees the above attack.
In my next article I will show you live step-by-step procedure to manipulate the packets and evade the IDS/IPS using scapy tool.
Thanks to Judy Novak for an outstanding discovery of above attack :)
Cheers,
Mozshetty
